Book Appointment
Schedule your appointment with simple form
Schedule your appointment with simple form
Our team of licensed and certified ayurveda
Our emergency Ayurveda services are designed to address
Our mission is to enhance the quality of life of our patients
years of experience
At Ebhaya, we are dedicated to providing natural and effective treatments for diseases through the wisdom of Ayurveda. By combining traditional practices with modern knowledge, we aim to improve the quality of life for our patients. Our treatments are designed to address the root causes of ailments through natural therapies, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications.
We have effective solutions for hair loss, Arthritis, Cerebral Palsy, weight loss, skin diseases like leucoderma, and dermatitis, and diabetes management through effective Ayurvedic practices.
Schedule your appointment with simple form
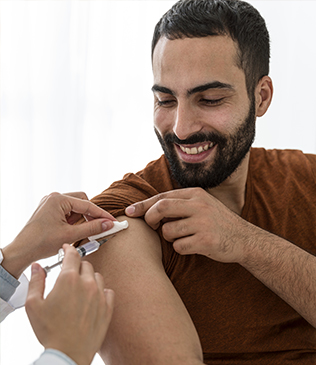











Type 1 diabetes, previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune condition in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Type 2 diabetes, formerly referred to as adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for the majority of cases. In type 2 diabetes, the body either becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes and insulin resistance lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, but affected individuals are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.




 3586+ reviews
3586+ reviews









Ebhaya's Ayurvedic treatments for diabetes focus on managing both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes effectively. Our remedies help regulate blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity, and preventing complications that improve overall health, providing a natural and safe alternative to conventional treatments
We understand that injuries and acute pain can unexpectedly.
We understand that injuries and acute pain can unexpectedly.
We understand that injuries and acute pain can unexpectedly.
We understand that injuries and acute pain can unexpectedly.
We understand that injuries and acute pain can unexpectedly.
We understand that injuries and acute pain can unexpectedly.

We understand that injuries and acute pain can happen unexpectedly. Our emergency Ayurveda services are designed to provide prompt and effective care to help you manage.
Hair Loss
Weight Loss
Diabetes
Skin Psoriasisn
Leucoderma
Eczema
Dermatitis
Osteoarthritis